Solar Panels
Solar panels are a popular and sustainable solution for generating electricity. They work by converting sunlight into electrical energy that can be used to power homes, businesses, and even entire communities. If you’re interested in installing solar panels on your property or just want to learn more about this technology, here is some helpful information on solar panels:
1: What are solar panels?
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They are made up of solar cells, which are made from semiconducting materials like silicon. When sunlight hits these cells, it creates an electric field that generates a flow of electrons, producing a direct current (DC) of electricity.
2: How do solar panels work?
Solar panels work by capturing sunlight and converting it into electrical energy. The process starts with the photovoltaic cells, which are arranged in a grid-like pattern on the panel. These cells are made of silicon, which is a semiconductor material that can absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity.
When sunlight hits the solar panels, the energy from the photons in the sunlight is absorbed by the solar cells. This energy knocks electrons in the silicon atoms loose, allowing them to flow freely through the cell. This flow of electrons generates a direct current (DC) of electricity, which can be used immediately or stored in batteries for later use.
3: What are the benefits of solar panels?
Solar panels offer several benefits, including:
- Lower electricity bills: Once installed, solar panels can help you save money on your electricity bills by generating your own electricity.
- Reduced carbon footprint: Solar energy is a clean, renewable energy source that produces no greenhouse gas emissions, helping to reduce your carbon footprint.
- Increased home value: Installing solar panels can increase the value of your home, making it more attractive to potential buyers.
- Energy independence: Generating your own electricity with solar panels can help you become more energy independent and less reliant on traditional energy sources.
- Long lifespan: Solar panels have a lifespan of up to 25-30 years, making them a durable and long-lasting investment.
4:How much do solar panels cost?
The cost of solar panels can vary depending on several factors, including the size of the
Top of Form
Regenerate response
Bottom of Form
Inverter
If you are interested in installing solar panels on your property, you will also need to consider the type of solar inverter you will use. The solar inverter is an essential component of any solar power system, as it is responsible for converting the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used to power your home or business. There are two main types of solar inverters: hybrid and non-hybrid. Here’s a breakdown of the differences between the two:
1: Non-hybrid solar inverters
Non-hybrid solar inverters are the most common type of inverter used in solar power systems. They are designed to work with traditional electricity grids and are not capable of storing excess solar energy. This means that any excess electricity generated by your solar panels during the day will be sent back to the grid, and you will receive credits for this energy that can be used to offset your electricity bills.
Non-hybrid inverters are generally less expensive than hybrid inverters, making them a more affordable option for homeowners who are looking to install solar panels. However, they do not provide backup power during a power outage, which can be a significant drawback for those living in areas with frequent power outages.
2: Hybrid solar inverters
Hybrid solar inverters, also known as battery-ready inverters, are designed to work with both solar panels and energy storage systems like batteries. This allows you to store excess solar energy generated during the day for use during times when your solar panels are not producing enough electricity, such as at night or during a power outage.
Hybrid inverters are more expensive than non-hybrid inverters, but they offer several benefits, including:
- Backup power: With a battery storage system, hybrid inverters can provide backup power during a power outage, ensuring that you have access to electricity when you need it.
- Energy independence: By storing excess solar energy, you can become more energy independent and rely less on the traditional electricity grid.
- Greater control over energy usage: With a hybrid inverter and energy storage system, you can control how much energy you use from your solar panels and how much you store for later use.
- Reduced electricity bills: By using stored solar energy during peak hours when electricity rates are high, you can reduce your electricity bills even further.
In summary, non-hybrid solar inverters are a good option for homeowners looking to save money on their electricity bills, while hybrid solar inverters are ideal for those who want to become more energy independent and have backup power during outages. It’s important to consider your energy needs and budget when choosing the right solar inverter for your solar power system.
Top of Form


Battery or storage system
If you’re considering adding a solar battery to your home or business’s solar power system, there are several factors to consider, including the type of battery and the method of connection. One important decision is whether to use an AC-coupled or DC-coupled system, as well as whether to use a high-voltage or low-voltage system. Here’s a breakdown of the differences between each type:
1: AC-coupled solar batteries
AC-coupled solar batteries are connected to the AC side of the solar power system, meaning they are installed between the solar panels and the existing electrical system. This allows the battery to store excess energy generated by the solar panels, which can be used later when the panels are not generating enough energy. AC-coupled systems are typically easier to install than DC-coupled systems, as they do not require additional equipment to be installed on the DC side of the system.
2: DC-coupled solar batteries
DC-coupled solar batteries are connected to the DC side of the solar power system, meaning they are installed between the solar panels and the solar inverter. This allows the battery to store excess energy generated by the solar panels before it is converted to AC electricity by the inverter. DC-coupled systems are typically more efficient than AC-coupled systems, as they reduce energy losses due to conversions from DC to AC.
3: High-voltage solar batteries
High-voltage solar batteries use a higher voltage range than standard batteries, typically between 350V to 800V DC. This allows the battery to store more energy and reduces the amount of cabling required, which can lower installation costs. High-voltage batteries are also more efficient and can charge and discharge at a faster rate.
4: Low-voltage solar batteries
Low-voltage solar batteries use a lower voltage range than standard batteries, typically between 12V to 48V DC. This makes them a more affordable option, but they have a lower capacity and are less efficient than high-voltage batteries. Low-voltage batteries also require more cabling, which can increase installation costs.
In summary, AC-coupled solar batteries are easier to install but less efficient than DC-coupled batteries. High-voltage batteries offer higher capacity and faster charging and discharging, while low-voltage batteries are more affordable but have lower capacity and efficiency. When choosing a solar battery, it’s important to consider your energy needs, budget, and the specific requirements of your solar power system.
Top of Form
Regenerate response
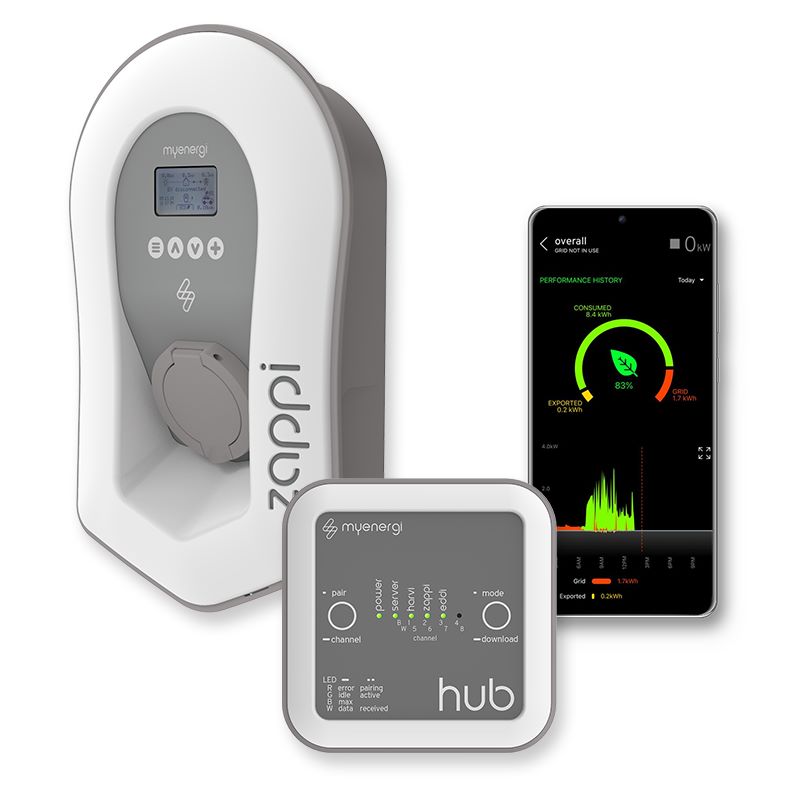
EV charger
As electric vehicles become more popular, many people are considering installing an electric vehicle (EV) charger at home or at their business. When it comes to installing an EV charger, there are two main options: connecting the charger to an existing solar inverter or using a standalone charger. Here’s a breakdown of the differences between the two options:
1: EV chargers connected to a solar inverter
EV chargers can be connected to an existing solar inverter that is used for a solar power system. This allows the EV to be charged using solar energy, reducing the reliance on the grid and saving money on electricity bills. In this setup, the EV charger is connected to the inverter, which is then connected to the solar panels on the roof. The solar panels generate electricity, which is then used to power the EV charger.
Connecting an EV charger to a solar inverter has several benefits, including:
- Cost savings: Using solar energy to charge your EV can significantly reduce your electricity bills, especially if you drive frequently or have multiple EVs.
- Environmentally friendly: Charging your EV using solar energy is a sustainable and environmentally friendly option that reduces your carbon footprint.
- Energy independence: By using solar energy to charge your EV, you become less reliant on the traditional electricity grid, increasing your energy independence.
2: Standalone EV chargers
Standalone EV chargers are separate units that are not connected to a solar inverter. They can be installed in any location where there is an electrical supply, such as in a garage or parking lot. Standalone EV chargers can be used with or without a solar power system.
Using a standalone EV charger has several benefits, including:
- Flexibility: Standalone EV chargers can be installed in any location where there is an electrical supply, giving you more flexibility in where you charge your EV.
- Compatibility: Standalone EV chargers are compatible with all types of EVs, making them a good option if you have multiple types of EVs.
- Future-proofing: Standalone EV chargers can be upgraded or replaced as needed, allowing you to future-proof your EV charging setup.
In summary, connecting an EV charger to a solar inverter allows you to charge your EV using solar energy, which can save money on electricity bills and reduce your carbon footprint. Standalone EV chargers offer more flexibility and future-proofing, but do not have the same cost savings or environmental benefits as solar-connected chargers. When deciding which option is best for you, consider your energy needs, budget, and the specific requirements of your EV and charging setup.
Top of Form